Introduction to Vaginal Warts
Vaginal warts, also known as genital warts, are benign lesions that commonly appear in and around the genital area due to an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus is one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) worldwide, with various types causing different health issues. While many individuals with HPV do not exhibit symptoms, some may develop vaginal warts, which can be concerning both physically and emotionally. Understanding the nature of Vaginal warts, their causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies is essential for everyone’s sexual health.
What Are Vaginal Warts?
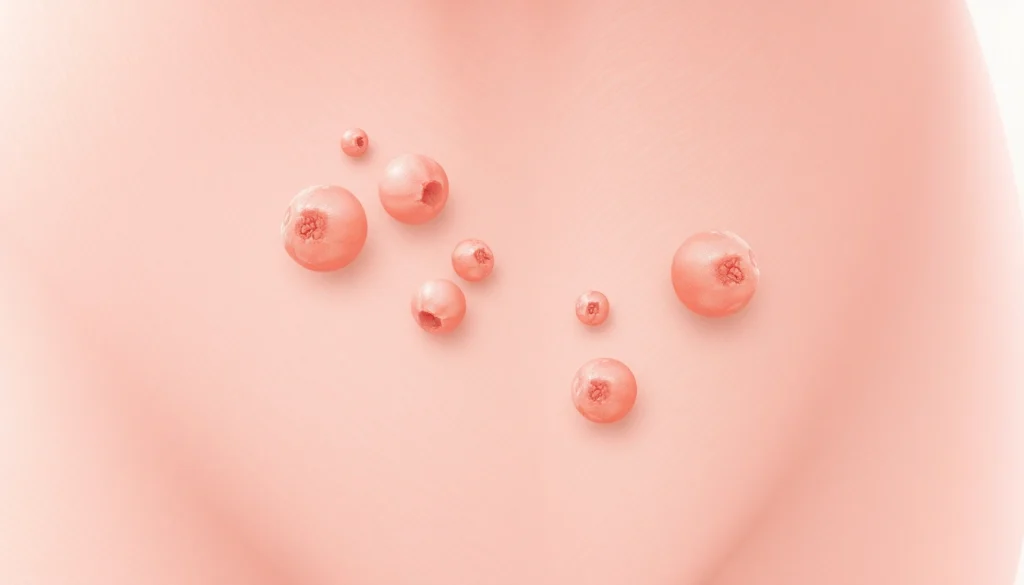
Vaginal warts manifest as small, fleshy growths or bumps on the genital region, including the vagina, vulva, and surrounding areas. They may vary in size and number and can be flesh-colored or slightly darker. Occasionally, they can take on a cauliflower-like texture or be smooth and round, depending on the type of HPV causing them. Importantly, while these warts are non-cancerous, they can still cause discomfort, itching, or irritation.
How Are Vaginal Warts Caused?
Vaginal warts are primarily caused by specific strains of HPV, notably types 6 and 11, which are responsible for the majority of genital warts cases. Transmission occurs through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, making it possible to contract the virus even if the infected person exhibits no visible warts. It is also worth noting that HPV is highly contagious, and individuals can carry the virus for years—even decades—before experiencing any symptoms. Immunocompromised individuals or those with multiple sexual partners may be at higher risk of contracting HPV and developing vaginal warts.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of vaginal warts is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for timely treatment, reducing the chance of further complications. Early diagnosis can also help prevent the spread of HPV to sexual partners. Moreover, it can alleviate anxiety and uncertainty surrounding abnormal growths in the genital area, as proper identification by a healthcare provider ensures a clear understanding of the condition. Regular health check-ups, especially for sexually active individuals, are vital for early detection.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Vaginal Warts
Common Symptoms to Look For
Recognizing the symptoms of vaginal warts is the first step towards seeking medical attention. Common signs include:
- Small growths that may be raised or flat.
- Clusters of warts that can resemble cauliflower.
- Itching, discomfort, or irritation in the genital area.
- Bleeding during intercourse or abnormal discharge.
- Changes in the appearance of the skin around the warts.
While these symptoms can indicate the presence of vaginal warts, they may also resemble other conditions, making it essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Visual Differences: Vaginal Warts vs. Other Conditions
It is important to differentiate vaginal warts from other similar conditions such as skin tags, bacterial vaginosis, or yeast infections. Vaginal warts tend to have a distinctive appearance, whereas other conditions may present with additional symptoms like unusual discharge, strong odors, or discomfort. If there is any doubt about the nature of the growths or symptoms, a professional examination is recommended to ensure proper identification and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Individuals should seek medical advice if they notice any unusual growths or persistent symptoms in the genital area. Additionally, if any existing warts change in appearance, grow in size, or become painful, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Early consultation can prevent complications and offers peace of mind by addressing any potential health concerns.
Diagnosis of Vaginal Warts
Methods of Diagnosis
Diagnosing vaginal warts typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. They may visually inspect the genital area for growths and inquire about symptoms and medical history. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions or to confirm the presence of HPV. Additionally, HPV typing tests may be conducted to determine the specific strain of the virus, especially if there is a need to assess cancer risk.
Preparing for Your Medical Appointment
Preparation for a medical appointment regarding vaginal warts can enhance the experience and ensure all concerns are addressed. Consider the following tips:
- Take note of any symptoms, including their duration, appearance, and any triggers or alleviating factors.
- Prepare a list of medications you are currently taking or have recently taken.
- Be ready to discuss your sexual health history and any recent partners, as this helps in understanding the potential exposure to HPV.
Being prepared can facilitate a more productive conversation with your healthcare provider and lead to accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Test Results
Upon receiving test results, it is essential to understand what they mean. Positive results for HPV may lead to further discussions about the type of HPV involved and recommended treatment options. If a biopsy is performed, your doctor will discuss whether the growths are benign or require additional follow-up. It is vital to clarify any uncertainties regarding test results to ensure you have a comprehensive understanding of your health status.
Treatment Options for Vaginal Warts
Over-the-Counter Treatments
For some individuals, over-the-counter treatments may help manage vaginal warts, although these options are typically more effective for mild cases. Topical solutions containing salicylic acid or trichloroacetic acid can help remove warts, but they should be used with caution as they can cause skin irritation. It is crucial to follow the instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare provider before initiating self-treatment to avoid complications.
Prescription Treatments and Procedures
More significant or persistent cases may require prescription treatments or procedures performed by a healthcare professional. Options include:
- Topical imiquimod, which stimulates the immune system to fight HPV.
- Podophyllin and podofilox, which help remove warts through chemical action.
- Cryotherapy, which involves freezing off the warts using liquid nitrogen.
- Electrosurgery, which uses heat to destroy warts.
- Laser treatment, which uses focused light to remove warts.
Discussing all available treatment options with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the most appropriate course of action tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Aftercare and Follow-Up
Post-treatment care for vaginal warts is crucial in ensuring effectiveness and preventing recurrence. Patients should closely follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding aftercare, including keeping the area clean and allowing time for healing. Regular follow-up appointments may be recommended to monitor for any signs of recurrence and manage any ongoing concerns.
Preventing Vaginal Warts
Effective Prevention Strategies
Prevention is key to avoiding vaginal warts and reducing the risk of HPV transmission. Practicing safe sex is the primary method of prevention. This includes:
- Using condoms during sexual activity, although this does not provide complete protection against HPV due to the potential for skin contact.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners to decrease exposure risk.
- Engaging in mutual monogamy with an uninfected partner.
Vaccination Against HPV
Vaccination against HPV is a highly effective strategy in preventing the virus and its associated diseases, including vaginal warts. The HPV vaccine is recommended for preteens but can be given to individuals up to 45 years of age. It protects against the most common cancer-causing and wart-causing strains of HPV, significantly reducing the prevalence of cases.
Maintaining Sexual Health
Maintaining good sexual health involves regular screenings for STIs, open communication with partners regarding sexual health history, and being proactive in seeking medical advice for any concerns. Education about HPV and its transmission can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their sexual practices, contributing to overall health and well-being.